Product Information
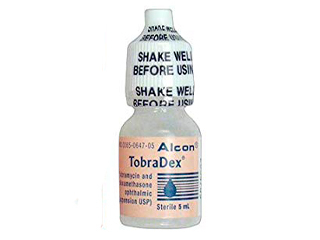
Experience Clearer Vision and Faster Relief with Tobramycin and Dexamethasone: Your Solution for Ocular Infections
Problem Description: The Pervasive Threat of Ocular Infections
Ocular infections represent a significant public health concern, capable of causing discomfort, vision impairment, and, in severe cases, permanent damage. Conditions such as bacterial conjunctivitis, blepharitis, and post-operative inflammation demand swift, effective treatment. The presence of harmful bacteria, often resilient to less potent therapies, necessitates a combination approach that attacks the infection while simultaneously managing the inflammatory response. Many patients search online for best eye drops for bacterial conjunctivitis, hoping for a quick resolution to their painful symptoms. When a simple antibiotic like Amoxicillin might be insufficient for localized, sensitive eye tissues, a targeted dual-action therapy becomes crucial. Untreated or poorly managed eye infections can lead to chronic irritation and recurrent issues, making the choice of medication paramount. We understand the urgency behind queries like how long does it take for tobramycin dexamethasone to work, as patients seek assurance that their chosen treatment is both powerful and rapid-acting.
The dual nature of many eye ailments—infection coupled with inflammation—means that treating only one aspect often leads to suboptimal results or prolonged recovery. For instance, an infection causes redness and discharge, but the accompanying swelling and pain are often due to the body's inflammatory reaction. Relying solely on a single-action antibiotic, such as attempting to treat with a systemic drug perhaps related to Rifampin, may not provide the necessary concentration of active ingredients directly at the site of infection in the eye. This is where sophisticated, formulated therapies shine. Understanding the landscape of available treatments, from older standards to newer combinations, helps patients realize the advantage of a specialized formulation designed specifically for ophthalmic use.
How the Medication Helps: The Power of Combination Therapy
Tobramycin and Dexamethasone offers a scientifically advanced solution by combining two potent active ingredients: Tobramycin, a broad-spectrum aminoglycoside antibiotic, and Dexamethasone, a potent corticosteroid. Tobramycin excels at eradicating a wide range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria commonly responsible for ocular infections. Its mechanism involves interfering with bacterial protein synthesis, effectively halting their growth and reproduction. This makes it highly effective against many common pathogens found in the eye. Many concerned parents type in pediatric dose for tobramycin dexamethasone eye drops, illustrating the need for reliable pediatric options supported by clear usage guidelines.
Dexamethasone, on the other hand, addresses the inflammatory component. As a powerful glucocorticoid, it suppresses the release of inflammatory mediators, thereby reducing redness, swelling, pain, and photophobia associated with the infection or injury. This dual mechanism is incredibly advantageous. By controlling inflammation quickly, it not only alleviates patient discomfort sooner but also potentially enhances the penetration and efficacy of the antibiotic component. Unlike treatments focused solely on controlling bacterial spread, like some older macrolides or penicillin derivatives, this combination provides comprehensive management. Patients frequently research difference between tobramycin and tobramycin dexamethasone to understand this crucial added benefit of inflammation control.
Benefits: Why Choose Tobramycin and Dexamethasone?
The primary benefit of using Tobramycin and Dexamethasone lies in its synergistic action and high efficacy in treating complicated or persistent ocular bacterial infections accompanied by significant inflammation. Clinical studies consistently show faster resolution times when both infection and inflammation are addressed simultaneously compared to using either agent alone. This formulation is often preferred over treatments where one might consider switching to a different class of antibiotic, such as a fluoroquinolone like Levaquin, if initial inflammation is high. Furthermore, the convenience of applying one preparation instead of two separate drops—one antibiotic and one steroid—improves patient compliance, a critical factor in successful treatment outcomes. We often see users asking is tobramycin dexamethasone an antibiotic or steroid, highlighting the confusion that this powerful combination addresses.
Another significant advantage is its proven performance across various ophthalmic scenarios, including managing bacterial keratitis where corneal involvement demands aggressive anti-inflammatory action alongside bacterial eradication. While some individuals might initially consider simpler, over-the-counter options, the inclusion of Dexamethasone ensures that severe inflammation is managed robustly, something that over-the-counter preparations simply cannot achieve. For those experiencing recurring issues, knowing the proper sequence for managing flares is vital; this is why searching for how to switch from tobramycin to tobramycin dexamethasone occurs during treatment adjustments.
Efficacy against resistant strains is also a strong selling point. While bacterial resistance is an evolving challenge, the established profile of Tobramycin against many common ocular pathogens, when coupled with reduced inflammation allowing better tissue access, provides a strong therapeutic advantage. It represents a benchmark treatment standard against which other therapies might be compared, especially when traditional options, perhaps similar to Amoxicillin in general application but less suited for the eye, have failed. We encourage all potential users to investigate FDA approval for tobramycin dexamethasone to confirm its trusted status.
Safety and Side Effects: A Professional Assessment
As with any potent medication, understanding the safety profile of Tobramramycin and Dexamethasone is essential. Since this medication is designed for topical ophthalmic use (either as drops or ointment, depending on the specific formulation), systemic absorption is generally low. However, because it contains a corticosteroid (Dexamethasone), prolonged or improper use carries specific risks that must be understood. The most common side effects are typically localized: transient stinging or burning upon application, mild irritation, or temporary blurred vision. Users should always look up tobramycin dexamethasone side effects long term use to be fully informed.
More serious, though less common, risks associated specifically with topical corticosteroids include elevated intraocular pressure (IOP), leading to glaucoma, and the potential for posterior subcapsular cataract formation with extended treatment. Therefore, treatment duration must be strictly adhered to as prescribed by the eye care professional. If a patient is already using other medications for glaucoma, or if they have a history of steroid-induced IOP elevation, careful monitoring is non-negotiable. Furthermore, in cases where there is an undiagnosed viral infection, such as herpes simplex keratitis, the steroid component can exacerbate the viral proliferation, underscoring the importance of accurate initial diagnosis. This is a critical distinction compared to non-steroidal anti-inflammatories.
Patients should cease use and contact their physician immediately if they experience signs of hypersensitivity, severe eye pain, vision changes, or increasing discharge. While Tobramycin is generally well-tolerated, as with all aminoglycosides, there is a small theoretical risk of ototoxicity with extremely high systemic absorption, though this is rarely a concern with topical ophthalmic application. For comparison, while drugs like Clarithromycin address bacterial issues systemically, the topical nature of this product minimizes general systemic risk. Always discuss your full medical history, especially concerning other topical steroid use or known allergies, when seeking a prescription for Tobramycin and Dexamethasone.
Reviews/Social Proof: Real-World Confidence
The confidence placed in Tobramycin and Dexamethasone by both practitioners and patients speaks volumes about its reliability. Many testimonials highlight the rapid return to normal activity after treatment initiation. Patients often express relief after struggling with persistent symptoms that did not fully resolve with single-agent therapies. For example, one common theme in user feedback revolves around the quick reduction in morning crusting, prompting searches such as tobramycin dexamethasone drop vs ointment to decide on the best delivery method for their lifestyle. This real-world validation is powerful, especially when facing the uncertainty of an eye infection.
Practitioners frequently rely on this combination for managing post-surgical inflammation where infection risk is present, demonstrating its high standard of care. Furthermore, patients often compare their experiences, noting how much faster the relief came compared to prior treatments, perhaps similar to the standard recovery time they might expect after using a broad-spectrum oral agent like Cenmox for other infections. The general sentiment confirms that when both inflammation and infection are present, this dual therapy stands out. We encourage prospective buyers to look up where to buy tobramycin dexamethasone online safely, emphasizing the importance of obtaining it through legitimate, regulated channels to ensure product authenticity.
The documented success rates in clinical settings translate into high satisfaction among users who adhere to the prescribed regimen. This social proof confirms that choosing a medication targeting both core problems simultaneously is the most logical path to recovery. This combination is often the go-to when simpler alternatives fail to address the underlying inflammatory component complicating the bacterial fight, unlike treatments purely focused on systemic bacterial control, such as Principen.
Dosage and Administration: Precision for Optimal Results
The precise dosage of Tobramycin and Dexamethasone (commonly available in 0.1% Tobramycin / 0.3% Dexamethasone concentrations) is dictated entirely by the severity and location of the infection, as determined by a qualified ophthalmologist. For typical cases of bacterial conjunctivitis, the common instruction involves instilling one or two drops into the affected eye(s) four times daily. However, in more severe scenarios, such as acute bacterial keratitis, the frequency may be significantly increased initially, sometimes hourly, before being tapered down as symptoms improve. It is absolutely vital never to self-adjust the frequency or duration of treatment. Abrupt cessation, even when symptoms clear, can lead to a rebound effect or recurrence, especially since the Dexamethasone component requires careful tapering.
Understanding the different forms is also part of proper administration. The drops provide rapid delivery, while the ointment form often stays in contact with the ocular surface longer, sometimes preferred for nighttime application or for patients with severe dry eye components. Patients often inquire about can I use tobramycin dexamethasone for pink eye, and the answer is yes, provided it is bacterial pink eye accompanied by inflammation. Always ensure clean hand hygiene before opening the bottle and avoid touching the dropper tip to the eye or any other surface to maintain sterility—a crucial step in preventing further contamination.
FAQ Section
What is the active ingredient of Tobramycin and Dexamethasone?
The medication contains two active ingredients: Tobramycin, which is an antibiotic, and Dexamethasone, which is a potent corticosteroid used to reduce inflammation. This combination ensures both the bacterial cause and the inflammatory effects are treated simultaneously.
Can I use this medication if I have a viral eye infection?
No. You must not use Tobramycin and Dexamethasone for viral eye infections, particularly Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) keratitis. The steroid component (Dexamethasone) can significantly worsen viral replication and cause severe vision loss. A proper diagnosis by an eye care professional is mandatory before starting this treatment.
How long should I use Tobramycin and Dexamethasone?
The duration is highly variable, ranging from a few days to several weeks, depending on the diagnosis. Never use it longer than prescribed. Corticosteroids like Dexamethasone require a gradual taper to prevent rebound inflammation or IOP spikes. If you are considering switching to an alternative like Clindamycin for a follow-up, discuss this with your doctor.
Is there an alternative if I cannot tolerate steroids?
Yes, if steroid use is contraindicated due to IOP concerns, your doctor might prescribe a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) eye drop combined with Tobramycin, or simply Tobramycin alone if inflammation is minimal. They might consider alternatives such as Cefadroxil if oral therapy is deemed necessary for a different infection profile, but for targeted eye treatment, the steroid component is often key when inflammation is present.
What if I forget a dose of Tobramycin and Dexamethasone?
If you miss a dose, apply it as soon as you remember, unless it is nearly time for the next scheduled dose. In that case, skip the missed dose and continue with your regular schedule. Do not double the dose to catch up. Consistency is key, especially in the initial intensive phase.
Price and Where to Buy: Securing Your Supply
The cost of Tobramycin and Dexamethasone can vary based on insurance coverage, location, and whether you purchase the brand-name product or a generic equivalent (if available and prescribed). As this is a prescription medication, it must be dispensed by a licensed pharmacy following a valid prescription from an eye care provider. While the convenience of searching where can I buy tobramycin dexamethasone drops without prescription is tempting for some, doing so bypasses essential medical oversight necessary to manage the risks associated with the corticosteroid component.
We strongly advocate purchasing your medication from reputable, licensed pharmacies, whether local or online, to guarantee the quality, purity, and correct concentration (0.1/0.3%). Be cautious of significantly discounted prices from unverified international sources, as these products may be counterfeit or improperly stored, rendering them ineffective or dangerous. We are committed to providing you with the most effective solutions, and that starts with ensuring you receive legitimate pharmaceutical products, unlike unregulated products sometimes discussed in relation to older anti-tuberculosis drugs like Myambutol which have entirely different uses.
Investigating your insurance formulary is the first step in managing out-of-pocket costs. If you have high co-pays, exploring generic alternatives or manufacturer savings programs might be beneficial. Remember, while cost is a factor, the value of rapid, effective resolution of a potentially vision-threatening infection far outweighs minor cost savings gained by compromising on the quality or legitimacy of the drug.
Call to Action: Take the Next Step Towards Clearer Vision Today
Do not let an ocular infection compromise your sight or daily comfort any longer. Tobramycin and Dexamethasone provides the targeted, dual-action therapy proven to fight stubborn bacterial invaders while calming painful inflammation. If you are currently suffering from symptoms suggestive of bacterial conjunctivitis or post-operative swelling, schedule an appointment with your eye care specialist immediately to discuss if this highly effective formulation is right for you. Proper diagnosis ensures you receive the best treatment pathway, whether that is this combination or perhaps another targeted therapy like Avelox for certain resistant organisms.
We urge you to prioritize your ocular health. Discuss the comprehensive benefits of combined antibacterial and anti-inflammatory action with your physician today. Effective treatment starts with the right prescription.
Conclusion
Tobramycin and Dexamethasone stands out as a leading treatment for bacterial eye infections complicated by inflammation. Its combination of Tobramycin’s potent antibiotic action and Dexamethasone’s rapid anti-inflammatory effect ensures quicker symptom relief and faster microbiological clearance than single-agent therapies. While vigilance regarding steroid side effects is necessary, under professional guidance, it remains a safe and highly effective standard of care. Secure your prescription today and experience the decisive advantage of this dual-action ocular therapy.